Flutter is an SDK for building fast apps for different platforms. It comes with comprehensive development tools and streamlines designing high-performance UIs. Find out why Flutter is a top-quality and cost-effective alternative to native app development.
Flutter is Google’s open-source toolkit for developing high-fidelity cross-platform applications. It allows you to create native software for Android and iOS operating systems with a single codebase. In other words, you can build two separate applications for both platforms with only one framework, which simplifies and speeds up the app development process.
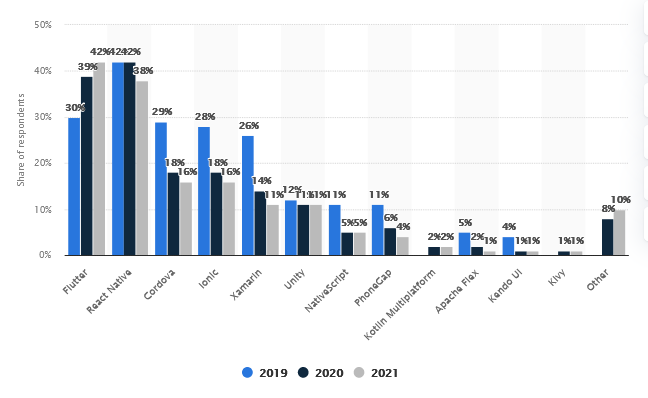
Flutter is typically used for mobile front-end development, but it also works for building web and desktop apps from the bottom to the top (or rather from the back to the front). Owing to its efficiency, reliability, and a number of other advantages, Flutter quickly made it to the first league. According to Statista, in 2021, it dethroned React Native as the most popular cross-platform mobile framework used by software developers worldwide.
A brief history of Flutter
The story of Flutter began in 2015 when Google unveiled Sky, the framework’s prototype, at the Dart Developer Summit. The company wanted to improve the screen refresh rate, boosting it from standard 60FPS to 120 FPS frequency.
It was a bold move, considering that at that time apps were rendered at 60FPS at most, but apparently, Google was looking further ahead. The giant also wanted to put to use its Dart programming language – designed as an object-oriented, improved alternative to JavaScript – which failed to score broader success since its release in 2011.
Soon, the framework was renamed to Flutter and released as alpha in 2017. On December 4 of the next year, Google rolled out its first stable, production-ready version. In the following years, the company introduced several enhancements and additions to its SDK, such as Metal API support for performance improvement on iOS devices, Material widgets, web-specific widgets, a new Canvas Kit renderer, and early-access desktop app support for Windows, Linux, and macOS, to name a few.
It didn’t take long before Flutter became the most successful implementation of Dart and rose to prominence as a handy, comprehensive toolset for building next-level UIs.
Flutter: widget-based development toolset
Flutter is usually referred to as a framework. In fact, Flutter’s architecture makes it a full-fledged software development kit (SDK). Designed as a layered system, Flutter SDK includes the Dart-based framework, a mobile-first rendering engine written in C/C++, platform-specific embedders, built-in widgets, APIs for unit and integration tests, and a comprehensive toolset for developing, testing, and compiling apps.
In Flutter, everything revolves around widgets, which are building blocks of user interface graphics. The framework comes with an out-of-the-box library of Material Design and Cupertino (iOS-style) widgets. Plus, there are tons of other options available in the widget catalog on the project’s website, where you can find all sorts of useful elements for streamlining UI development and delivering better user experience.
They include buttons, columns, containers, sliders, layout, styling, scrolling, animation, motion elements, and many more. Additionally, there is plenty of third-party libraries that allow Flutter developers to create great user interfaces more efficiently.
Examples include:
- GetWidget – one of the largest UI libraries comprising a 1000+ widget collection,
- Staggered GridView – a package for displaying pictures in a feed-like style,
- TimelineTile – a tool for building customizable timelines,
- Charts – a data visualization library, and many more.
Why build Flutter apps? Key advantages of Flutter app development
The main characteristic of Flutter is its cross-platform development capacity. Still, the framework wouldn’t earn its top status if it weren’t for its other advantages. So, what are the key benefits of using Flutter to develop apps?
Native-like performance and speed thanks to the Dart programming language
Flutter apps are praised for their speed matching native performance. According to CPU-intensive tests by inVerita, Flutter’s speed is comparable with Swift’s for iOS and slightly to moderately lower than native for Android. Still, in each test, Flutter outperformed React Native twice so by a factor of 10+. In short, the framework allows developers to build really fast iOS and Android apps that are on par with native apps for respective platforms.
One of the reasons for Flutter’s stellar performance is Dart, a client-optimized language that uses both ahead-of-time (AOT) and just-in-time (JIT) compilation, which speeds up the code execution and improves overall efficiency. Unlike React Native, which transpiles to native widgets, Flutter compiles Dart source code all the way to native code on iOS and Android platforms.
Another performance-enhancing feature is Flutter’s ability to control each pixel on the screen. React apps rely on the JavaScript bridge and may encounter issues while rendering large datasets.
Outstanding UI, brand-specific design created with customizable widgets
Flutter is a versatile framework, but it’s primarily used for building mobile interfaces – and that’s where it really excels. Thanks to its own rendering engine, a robust development toolkit, and an abundance of widgets, Google’s SDK provides developers with means to conjure impeccable, smooth, and fast UIs.
Flutter’s ecosystem distinct feature is high customizability which aligns with the Material Theming approach focused on providing brand-specific design. As a result, Flutter apps deliver outstanding UX and a unique feel that help them stand out from the crowd.
Faster app development enabled by a comprehensive toolkit
With Flutter, mobile app development is faster for a number of reasons:
- The framework’s cross-platform capacity makes it easier to create UIs for both iOS and Android platforms, saving you the time and costs related to native development.
- The pre-built libraries come with a wide selection of useful components, comprising stateless widgets, including Icon, IconButton, and Text, and stateful widgets, including Checkbox, Form, InkWell, Radio, and Slider.
- Flutter’s widget ecosystem is extremely flexible: elements can be mixed and reused, plus they fit any screen size.
- The Flutter framework provides an awesome function called hot reload. It enables experimenting with the interface, adding new features, fixing bugs, and analyzing changes in real time without altering the state of the app, which continues to execute from where it was before the hot reload command was run. As a result, developers can test and improve versions faster, contributing to a shorter time to market. It’s worth stressing that the hot reload feature makes Flatt a perfect tool for creating MVP apps.
It’s easy to learn! For a JS expert, Flutter development is a piece of cake
The Flutter “language” is considered easy to learn, which is an obvious asset. Setting up a Flutter team is simpler than onboarding, say, C++ developers, so you have less to worry about regarding recruitment, project continuity, work pace, and costs.
Developers experienced in creating mobile apps or web apps will quickly get a grasp of the framework. The C/C++ layer is very thin and nothing to worry about even for those with a JavaScript-only background, as Flutter implements most of the system in Dart – also a very approachable programming language.
The availability of learning resources and very detailed, example-rich documentation are also a big plus. Flutter’s inherent simplicity makes the whole effort a lot easier, as the framework provides a lot of advanced features, such as sensor data collection, GPS coordinates, and Bluetooth in ready-to-use plugins.
Does the Flutter framework have any downsides?
Flutter has even more advantages, both on general and detailed levels, making it a great choice for building apps for multiple platforms. But what about the downsides?
Well, a lot depends on your perspective, business needs, and IT environment. Some view Flutter as a still immature technology, arguing that many Flutter libraries are not safe enough for critical projects. Still, the framework is constantly perfected by Google, looking after the project and fixing bugs. It also has a vibrant and growing community contributing to Flutter’s evolution.
There is an issue with weight, though. Flutter app performance may be impressive, but so is the size – in the bad sense. Flutter applications need to include the framework’s engine and widgets. As a result, they are larger than native software for iOS or Android devices and consume a lot of space, not to mention they take longer to download or update.
The lack of web support has also been counted among the framework’s downsides. However, in 2021 Google released Flutter 2, containing stable web support focusing on progressive web applications, single page applications, and expanding existing Flutter apps to the web. Nevertheless, Flutter’s web-related layer is still in its infancy, and the framework is definitely more reliable for building mobile applications.
Should you consider Flutter for your business?
Flutter allows you to easily create apps with great UIs. Suffice to say, it helped to create Google Ads, Google Pay, Groupon, Alibaba’s Xianu app, eBay Motors, and dozens of other apps. However, there are other mobile and web development frameworks that can rival Flutter in some aspects. Apart from React Native, which has plenty of advantages of its own, they include Ionic, Xamarin, and Cordova, to name a few.
If you want to make sure you choose the right toolkit for your project to effectively achieve your business goals in the most efficient way, we’ll surely have some insights for you. Contact us anytime. We’ll be happy to discuss your priorities!













 +1 (888)
413 3806
+1 (888)
413 3806